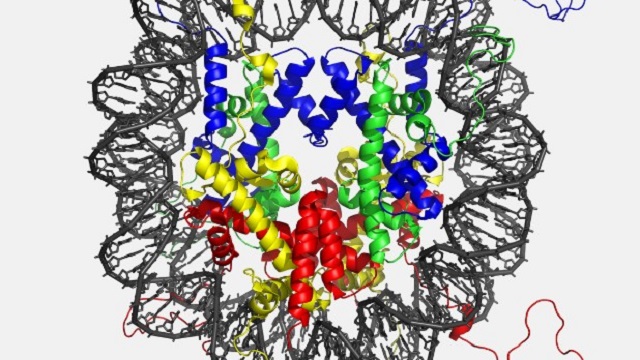
Chromatin: How DNA Fits and Controls Genes
DNA inside human cells is not just floating around freely. It is tightly
wrapped around small proteins, forming a long chain. The DNA loops around each
protein unit before moving to the next. This combination of DNA and proteins is
called chromatin. Chromatin helps nearly 2 meters of DNA fit inside a cell nucleus
that is only a few micrometres wide.
Chromatin does more than just pack DNA. Its structure also controls which genes
can be used and which stay turned off. Some areas of chromatin are loosely packed,
making it easy for the cell to read the DNA. Other areas are tightly packed,
making the DNA harder to access. Understanding how cells manage these different
states has been an important question in molecular biology.